Collaborative network
By Jérôme Pelletier
In 2022, the Executive Committee initiated a project to describe the collaboration network between regular GREZOSP members. The objective of this project is to compare the collaborations between members before the implementation of the funding agreement with the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA), period from 2017 to 2021, with the collaborations following its implementation, period starting in 2022 and ending in 2027. In the first phase of this project, 95 articles published from 2017 to 2021 on which at least 2 regular GREZOSP members were co-authors were retrieved from the Pubmed search engine (Figure 1). The authors of the articles were subsequently filtered to retain only regular GREZOSP members. Thus, a collaboration is defined as the fact that two members were co-authors on the same article. A collaboration network was built with the R bibliometrix plugin (1). The resulting network contains a total of 40 authors accounting for 314 collaborations (Figure 2).
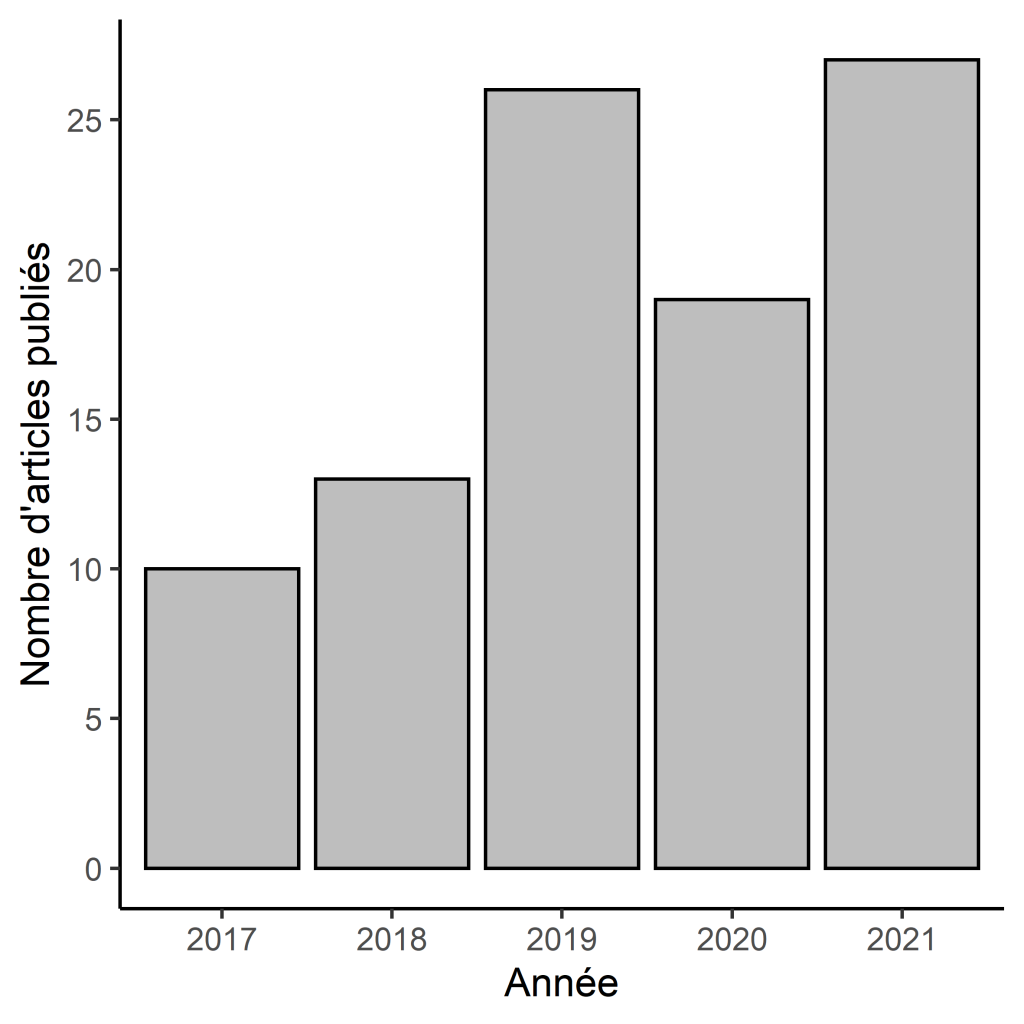
Figure 1 : Number of papers published per year between 2017 and 2021 with at least 2 regular GREZOSP member authors.
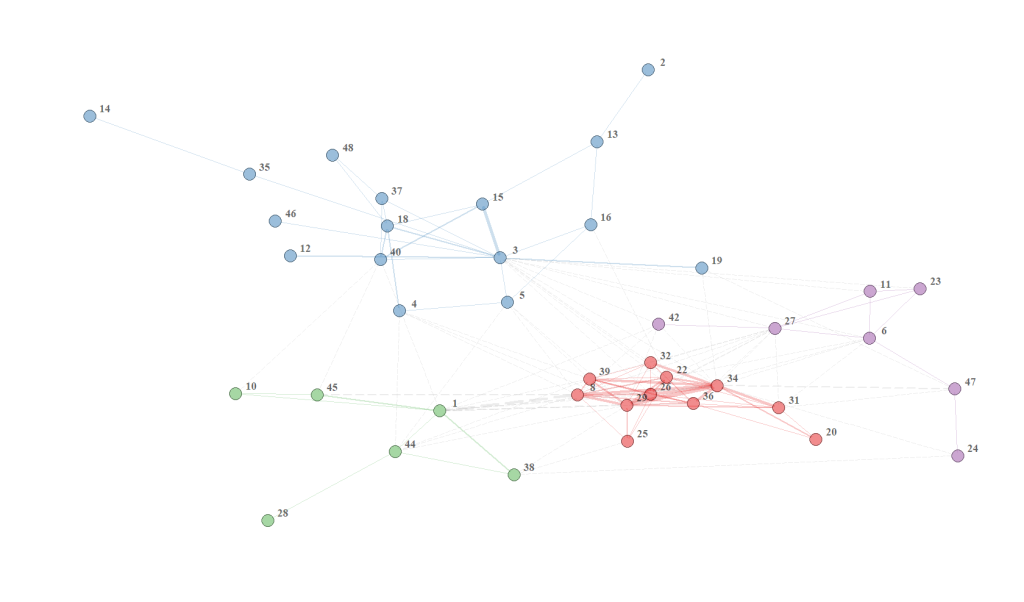
Figure 2 : Network of collaborations among regular GREZOSP members from 2017 to 2021. The thickness of the lines is proportional to the number of collaborations between 2 authors.
The density of the network, i.e. the number of links present between collaborators divided by the total number of possible links, is 17.6%. To aid visualization, the collaboration network was grouped into clusters using an algorithm using the Leuven method. The Leuven method compares the number of collaborations within an aggregate to the total number of collaborations between the aggregate and the rest of the network. Thus, an aggregate consists of a set of authors who have more collaborations with each other than with the other members of the network. Four clusters, blue, red, purple and green, with 16, 11, 7 and 6 authors respectively, were identified (Figure 2). To describe the evolution of collaborations between years, a network of collaborations was made for four overlapping periods: 2017-2018, 2018-2019, 2019-2020 and 2020-2021. The number of regular members who participated in the GREZOSP collaboration network was 22, 32, 34, and 35 for the 2017-2018, 2018-2019, 2019-2020, and 2020-2021 periods respectively (Figure 3).
Finally, the keywords of the publications included in this analysis were extracted to determine the main research themes. The individual keywords from the 2017-2021 publications were aggregated to determine their frequency and then represented in a word cloud (Figure 4). Among the most frequent keywords are certain disciplinary fields such as epidemiology (n=87), microbiology (n=61), genetics (n=57) and parasitology (n=28). This analysis also highlights the animal theme with keywords such as animals (n=62) or veterinary (n=32). Some health issues are frequent such as Lyme disease (n=19), transmission of infectious diseases (n=19) or bacterial resistance to antibiotics (n=9).
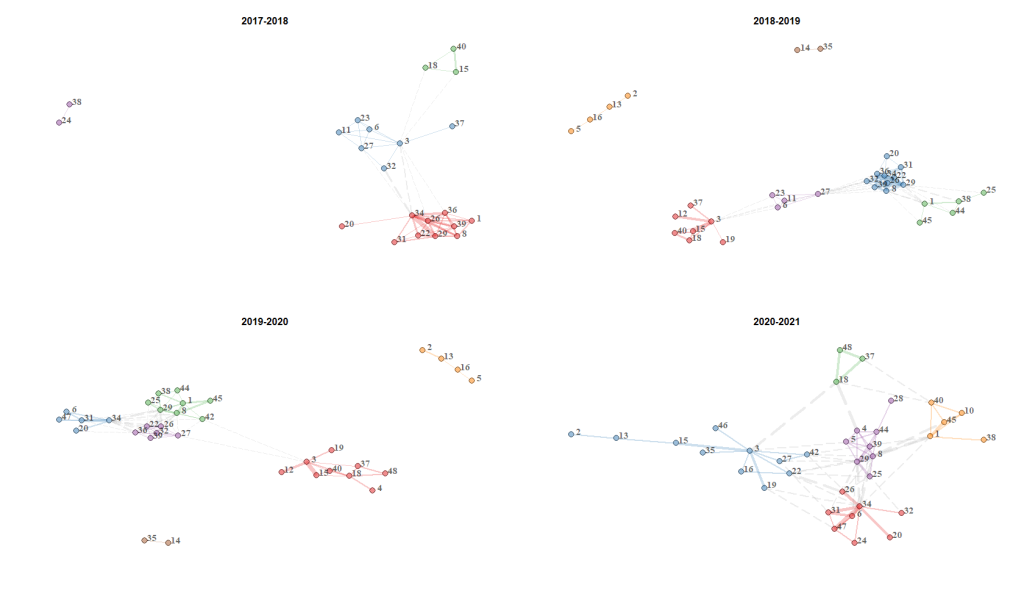
Figure 3 : Network of collaborations between regular GREZOSP members for 2017-2018, 2018-2019, 2019-2020, and 2020-2021. The thickness of the lines is proportional to the number of collaborations between 2 authors.

Figure 4 : Word cloud made from the keywords associated with the scientific publications included in this analysis. The size of the words in the graph is proportional to their frequency.
References
- Aria M, Cuccurullo C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics. 2017;11(4):959-75.

